
How can we work with sensors Android Tutorial
To monitor the three-dimensional device movement or to monitor the change in the environment of the device, the Sensors are used. In Android, we can work with different types of sensors, using the Sensor API.
Types of Sensors:
There are three types of sensors in Android. These are:
- Motion Sensors: To measure the acceleration forces and rotational forces along with three axes, the Motion Sensors are used in Android.
- Position Sensors: To measure the physical position of the device, the Position Sensors are used in Android.
- Environmental Sensors: To measure the environmental changes such as temperature, humidity, etc., the Environmental Sensors are used in Android.
Android Sensor API:
There are many classes and interfaces in the Android sensor API. We are going to discuss some of the important classes and interfaces of the sensor API.
SensorManager class:
To get sensor instances, to access and list sensors, and to register and unregister the sensor listeners and to serve many more such purposes, the methods of the android.hardware.SensorManager class are used. We can call the method getSystemService() and pass the SENSOR_SERVICE constant in it, to get the instance of the SensorManager.
Syntax:
SensorManager sm = (SensorManager)getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE); |
Sensor class:
To get the information about the sensor such as sensor name, sensor type, sensor resolution, sensor type, etc., in Android the android.hardware.Sensor class is used.
SensorEvent class:
The instance of the SensorEvent class is created by the system to provide information about the sensor.
SensorEventListener interface:
To get the information when the sensor values or sensor accuracy changes, two call back methods are provided by the SensorEventListener interface. These are:
- void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy): When the sensor accuracy is changed, this method is called.
- void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event): When the sensor values are changed, this method is called.
Example:
In the below example, we are using the Android Sensor API to print the x, y, and z axes values.
activity_main.xml:
In the activity_main.xml file, we will add a TextView.
|
Activity class:(File: MainActivity.java)
In the MainActivity.java file, we will write the code to print the values of the x axis, y axis, and z axis.
package com.example.radioapp;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
TextView tv1=null;
private SensorManager mSensorManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView2);
tv1.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
List mList= mSensorManager.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ALL);
for (int i = 1; i < mList.size(); i++) {
tv1.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
tv1.append("\n" + mList.get(i).getName() + "\n" + mList.get(i).getVendor() + "\n" + mList.get(i).getVersion());
}
}
} |
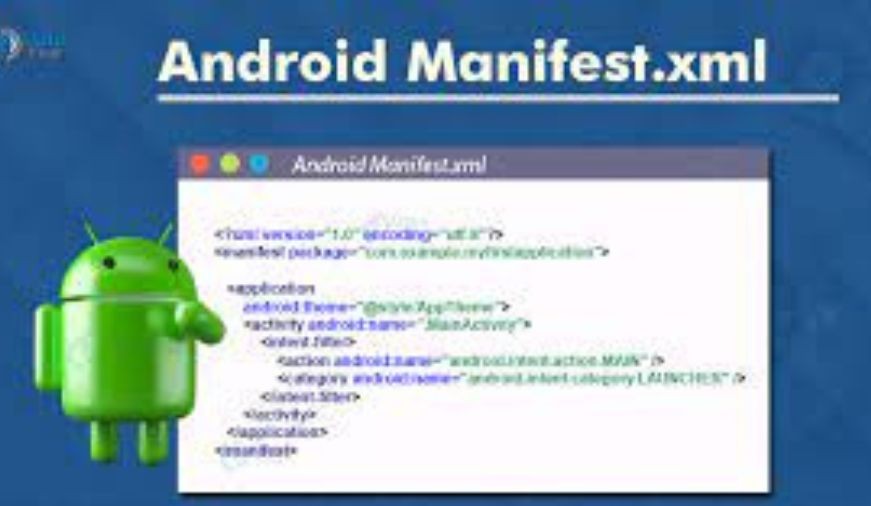
AndroidManifest.xml:
0 comments